一、项目介绍
1.2 项目硬件
-
ElfBoard ELF 1 开发板 -
WiFi(RTL8723DU) -
USB免驱摄像头 -
Linux服务器
1.3 软件环境
-
阿里云物联网平台 -
Nginx -
Python -
Flask
二、项目方案
2.2 数据检测与设备控制
三、数据检测与设备控制
传感器数据采集与上传
温湿度数据采集
#define AHT20_DEV "/dev/aht20"
int get_aht20(float* ath20_data)
{
int fd;
unsigned int databuf[2];
int c1,t1;
float hum,temp;
int ret = 0;
fd = open(AHT20_DEV, O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0) {
printf("can't open file %srn", AHT20_DEV);
return -1;
}
ret = read(fd, databuf, sizeof(databuf));
if(ret == 0) {
c1 = databuf[0]*1000/1024/1024;
t1 = databuf[1] *200*10/1024/1024-500;
hum = (float)c1/10.0;
temp = (float)t1/10.0;
printf("hum = %0.2f temp = %0.2f rn",hum,temp);
*ath20_data = hum;
*(ath20_data+1) = temp;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}电压数据采集
#define voltage5_raw "/sys/bus/iio/devices/iio:device0/in_voltage5_raw"
#define voltage_scale "/sys/bus/iio/devices/iio:device0/in_voltage_scale"
float get_adc(void)
{
int raw_fd, scale_fd;
char buff[20];
int raw;
double scale;
/* 1.打开文件 */
raw_fd = open(voltage5_raw, O_RDONLY);
if(raw_fd < 0){
printf("open raw_fd failed!n");
return -1;
}
scale_fd = open(voltage_scale, O_RDONLY);
if(scale_fd < 0){
printf("open scale_fd failed!n");
return -1;
}
/* 2.读取文件 */
// rewind(raw_fd); // 将光标移回文件开头
read(raw_fd, buff, sizeof(buff));
raw = atoi(buff);
memset(buff, 0, sizeof(buff));
// rewind(scale_fd); // 将光标移回文件开头
read(scale_fd, buff, sizeof(buff));
scale = atof(buff);
printf("ADC原始值:%d,电压值:%.3fVrn", raw, raw * scale / 1000.f);
close(raw_fd);
close(scale_fd);
return raw * scale / 1000.f;
}LED状态采集与控制
#define LED1_BRIGHTNESS "/sys/class/leds/led1/brightness"
#define LED2_BRIGHTNESS "/sys/class/leds/led2/brightness"
int get_led(int led_sel)
{
int led;
char buff[20];
int state=0;
if(led_sel == 2)
{
led=open(LED2_BRIGHTNESS, O_RDWR);
}else{
led=open(LED1_BRIGHTNESS, O_RDWR);
}
if(led<0)
{
perror("open device led error");
exit(1);
}
read(led, buff, sizeof(buff));
state = atoi(buff);
close(led);
return state;
}
void set_led(int led_sel, char state)
{
int led;
if(led_sel == 2)
{
led=open(LED2_BRIGHTNESS, O_RDWR);
}else{
led=open(LED1_BRIGHTNESS, O_RDWR);
}
if(led<0)
{
perror("open device led error");
exit(1);
}
write(led, &state, 1);//0->48,1->49
close(led);
}自动化控制
当ADC采集的电压大于阈值2.5V时自动开启LED1,低于时自动关闭LED1。
if(adc>2.5){
set_led(1,'1');
}else{
set_led(1,'0');
}数据上传
在main函数的while(1)中
adc=get_adc();
get_aht20(ath20_data);
led1_state = get_led(1);
led2_state = get_led(2)>0?1:0;
demo_send_property_post(dm_handle, "{"temperature": 21.1}");
sprintf(data_str,"{"Voltage": %.3f}", adc);
demo_send_property_post(dm_handle, data_str);
memset(data_str, 0, sizeof(data_str));
sprintf(data_str,"{"Humidity": %.3f}", ath20_data[0]);
demo_send_property_post(dm_handle, data_str);
memset(data_str, 0, sizeof(data_str));
sprintf(data_str,"{"temperature": %.3f}", ath20_data[1]);
demo_send_property_post(dm_handle, data_str);
memset(data_str, 0, sizeof(data_str));
sprintf(data_str,"{"LEDSwitch": %d}", led1_state);
demo_send_property_post(dm_handle, data_str);
memset(data_str, 0, sizeof(data_str));
sprintf(data_str,"{"LEDSwitch2": %d}", led2_state);
demo_send_property_post(dm_handle, data_str);云端指令响应
添加cJSON
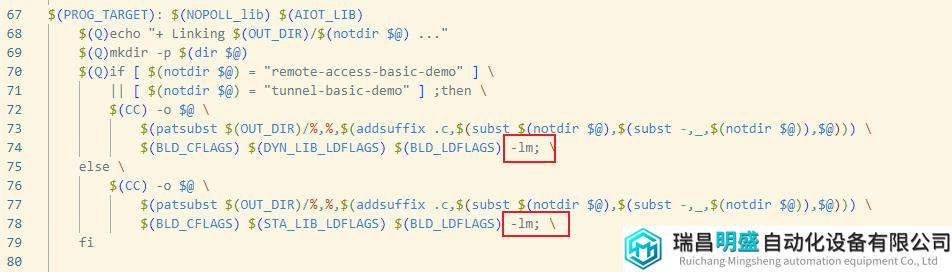
修改Makefile
实现代码
static void demo_dm_recv_property_set(void *dm_handle, const aiot_dm_recv_t *recv, void *userdata)
{
int led;
char state=0;
printf("demo_dm_recv_property_set msg_id = %ld, params = %.*srn",
(unsigned long)recv->data.property_set.msg_id,
recv->data.property_set.params_len,
recv->data.property_set.params);
/* TODO: 以下代码演示如何对来自云平台的属性设置指令进行应答, 用户可取消注释查看演示效果 */
cJSON* cjson_result = NULL;
cJSON* cjson_set1 = NULL;
cJSON* cjson_set2 = NULL;
cjson_result = cJSON_Parse(recv->data.property_set.params);
if(cjson_result == NULL)
{
printf("parse fail.n");
return;
}
//{"LEDSwitch":0}
cjson_set1 = cJSON_GetObjectItem(cjson_result,"LEDSwitch");
if(cjson_set1)
{
printf("LED1 set %dn",cjson_set1->valueint);
state = cjson_set1->valueint+48;
led=open(LED1_BRIGHTNESS, O_WRONLY);
if(led<0)
{
perror("open device led1");
exit(1);
}
write(led, &state, 1);//0->48,1->49
close(led);
}
cjson_set2 = cJSON_GetObjectItem(cjson_result,"LEDSwitch2");
if(cjson_set2){
printf("LED2 set %dn",cjson_set2->valueint);
state = cjson_set2->valueint+48;
led=open(LED2_BRIGHTNESS, O_WRONLY);
if(led<0)
{
perror("open device led1");
exit(1);
}
write(led, &state, 1);//0->48,1->49
close(led);
}
//释放内存
cJSON_Delete(cjson_result);
{
aiot_dm_msg_t msg;
memset(&msg, 0, sizeof(aiot_dm_msg_t));
msg.type = AIOT_DMMSG_PROPERTY_SET_REPLY;
msg.data.property_set_reply.msg_id = recv->data.property_set.msg_id;
msg.data.property_set_reply.code = 200;
msg.data.property_set_reply.data = "{}";
int32_t res = aiot_dm_send(dm_handle, &msg);
if (res < 0) {
printf("aiot_dm_send failedrn");
}
}
}四、视频监控
RTMP服务器搭建
./configure --add-module=/usr/local/nginx/nginx-http-flv-module
make&&make install安装完成后,需要进入Nginx安装目录(默认为/usr/local/nginx/),并在conf文件夹下对nginx.conf文件进行修改,增加rtmp功能(注意需要打开服务器的1935端口):
worker_processes 1;
#worker_processes auto;
#worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;
#worker_cpu_affinity auto;
error_log logs/error.log error;
events {
worker_connections 4096;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
location / {
root html;
index index.html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
location /live {
flv_live on; #打开 HTTP 播放 FLV 直播流功能
chunked_transfer_encoding on; #支持 'Transfer-Encoding: chunked' 方式回复
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' '*'; #添加额外的 HTTP 头
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true'; #添加额外的 HTTP 头
}
location /hls {
types {
application/vnd.apple.mpegurl m3u8;
video/mp2t ts;
}
root /tmp;
add_header 'Cache-Control' 'no-cache';
}
location /dash {
root /tmp;
add_header 'Cache-Control' 'no-cache';
}
location /stat {
rtmp_stat all;
rtmp_stat_stylesheet stat.xsl;
}
location /stat.xsl {
root /var/www/rtmp;
}
location /control {
rtmp_control all;
}
}
}
rtmp_auto_push on;
rtmp_auto_push_reconnect 1s;
rtmp_socket_dir /tmp;
rtmp {
out_queue 4096;
out_cork 8;
max_streams 128;
timeout 1s;
drop_idle_publisher 1s;
log_interval 5s;
log_size 1m;
server {
listen 1935;
server_name xxx.xxx.xx; #填入你自己的域名
application myapp {
live on;
gop_cache on;
}
application hls {
live on;
hls on;
hls_path /tmp/hls;
}
application dash {
live on;
dash on;
dash_path /tmp/dash;
}
}
}
最后启动Nginx服务,即可完成RTMP服务器的搭建:
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
./nginx本地推流
ffmpeg -f video4linux2 -r 5 -s 320x240 -i /dev/video2 -c:v libx264 -preset ultrafast -tune zerolatency -r 5 -f flv rtmp://xxx.xxxxxx.xxx/live/test框架
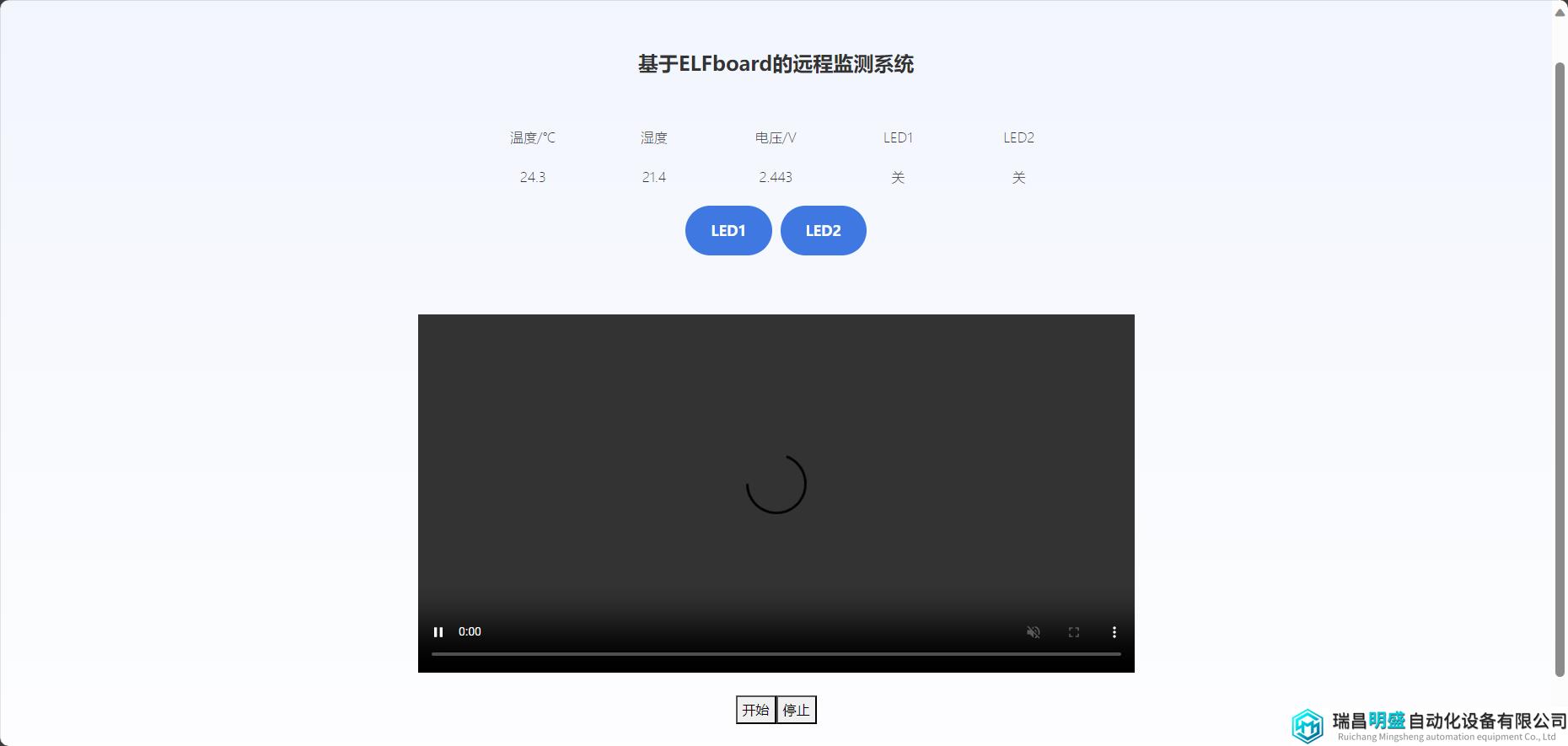
视频拉流
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/flv.js/1.5.0/flv.js"></script>之后设计Web页面播放器,具体代码如下:
<div class="row mt-10">
<div class="col-lg-8 mx-auto">
<video id="videoElement" class="img-fluid" controls autoplay width="1024" height="576" muted>
Your browser is too old which doesn't support HTML5 video.
</video>
</div>
<!-- /column -->
</div>
<br>
<div class="d-flex justify-content-center">
<!--<button οnclick="flv_load()">加载</button>-->
<button onclick="flv_start()">开始</button>
<button onclick="flv_pause()">停止</button>
</div><script type="text/javascript">
var player = document.getElementById('videoElement');
if (flvjs.isSupported()) {
var flvPlayer = flvjs.createPlayer({
type: 'flv',
url: 'http://xxx.xxxxx.xx/live?port=1935&app=myapp&stream=test',
"isLive": true,
hasAudio: false,
hasVideo: true,
//withCredentials: false,
//cors: true
}, {
enableWorker: true,
enableStashBuffer: false,
lazyLoad: false,
lazyLoadMaxDuration: 0,
lazyLoadRecoverDuration: 0,
deferLoadAfterSourceOpen: false,
fixAudioTimestampGap: true,
autoCleanupSourceBuffer: true,
});
flvPlayer.attachMediaElement(videoElement);
flvPlayer.load(); //加载
flv_start();
}
function flv_start() {
player.play();
}
function flv_pause() {
player.pause();
}
</script>远程数据的读取与指令下发
class Sample:
def __init__(self):
pass
@staticmethod
def create_client(
access_key_id: str,
access_key_secret: str,
) -> OpenApiClient:
"""
使用AK&SK初始化账号Client
@param access_key_id:
@param access_key_secret:
@return: Client
@throws Exception
"""
config = open_api_models.Config(
# 必填,您的 AccessKey ID,
access_key_id=access_key_id,
# 必填,您的 AccessKey Secret,
access_key_secret=access_key_secret
)
# Endpoint 请参考 https://api.aliyun.com/product/Iot
config.endpoint = f'iot.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com'
return OpenApiClient(config)
@staticmethod
def create_set_info() -> open_api_models.Params:
"""
API 相关
@param path: params
@return: OpenApi.Params
"""
params = open_api_models.Params(
# 接口名称,
action='SetDeviceProperty',
# 接口版本,
version='2018-01-20',
# 接口协议,
protocol='HTTPS',
# 接口 HTTP 方法,
method='POST',
auth_type='AK',
style='RPC',
# 接口 PATH,
pathname=f'/',
# 接口请求体内容格式,
req_body_type='formData',
# 接口响应体内容格式,
body_type='json'
)
return params
@staticmethod
def create_get_info() -> open_api_models.Params:
"""
API 相关
@param path: params
@return: OpenApi.Params
"""
params = open_api_models.Params(
# 接口名称,
action='QueryDeviceOriginalPropertyStatus',
# 接口版本,
version='2018-01-20',
# 接口协议,
protocol='HTTPS',
# 接口 HTTP 方法,
method='POST',
auth_type='AK',
style='RPC',
# 接口 PATH,
pathname=f'/',
# 接口请求体内容格式,
req_body_type='formData',
# 接口响应体内容格式,
body_type='json'
)
return params
@staticmethod
def main():
client = Sample.create_client(access_key_id, access_key_secret)
params = Sample.create_get_info()
# query params
queries = {}
queries['PageSize'] = 10
queries['ProductKey'] = 'xxxxxxxxxx'
queries['DeviceName'] = 'xxxx'
queries['Asc'] = 0
# body params
body = {}
body['ApiProduct'] = None
body['ApiRevision'] = None
# runtime options
runtime = util_models.RuntimeOptions()
request = open_api_models.OpenApiRequest(
query=OpenApiUtilClient.query(queries),
body=body
)
# 复制代码运行请自行打印 API 的返回值
# 返回值为 Map 类型,可从 Map 中获得三类数据:响应体 body、响应头 headers、HTTP 返回的状态码 statusCode。
response = client.call_api(params, request, runtime)
body = response['body']
Data = body['Data']
List = Data['List']
Proper = List['PropertyStatusDataInfo']
Temp = json.loads(Proper[0]['Value'])
Volt = json.loads(Proper[1]['Value'])
Led2 = json.loads(Proper[2]['Value'])
Led1 = json.loads(Proper[3]['Value'])
Humi = json.loads(Proper[4]['Value'])
message = {
'humi': Humi['data'],
'temp': Temp['data'],
'volt': Volt['data'],
'led1': Led1['data'],
'led2': Led2['data'],
}
return jsonify(message)
@staticmethod
def main_set(item: str):
client = Sample.create_client(access_key_id, access_key_secret)
params = Sample.create_set_info()
# query params
queries = {}
queries['ProductKey'] = 'xxxxxxxxxxxx'
queries['DeviceName'] = 'xxxx'
queries['Items'] = item # '{"LEDSwitch":0}'
# body params
body = {}
body['ApiProduct'] = None
body['ApiRevision'] = None
# runtime options
runtime = util_models.RuntimeOptions()
request = open_api_models.OpenApiRequest(
query=OpenApiUtilClient.query(queries),
body=body
)
# 复制代码运行请自行打印 API 的返回值
# 返回值为 Map 类型,可从 Map 中获得三类数据:响应体 body、响应头 headers、HTTP 返回的状态码 statusCode。
resp = client.call_api(params, request, runtime)
body = resp['body']
data = body['Success']
return str(data)
2024年1月22日
Categories: